About The GMAT Integrated Reasoning
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a standardized assessment widely used by business schools to evaluate the qualifications of applicants for advanced study in business and management.

A critical component of the GMAT is the Integrated Reasoning (IR) section, introduced to measure a candidate’s ability to evaluate information presented in multiple formats from various sources. This section is designed to reflect the kind of complex decision-making and data analysis skills essential in today’s business environment.
Table of Contents
Overview of the GMAT Integrated Reasoning Section
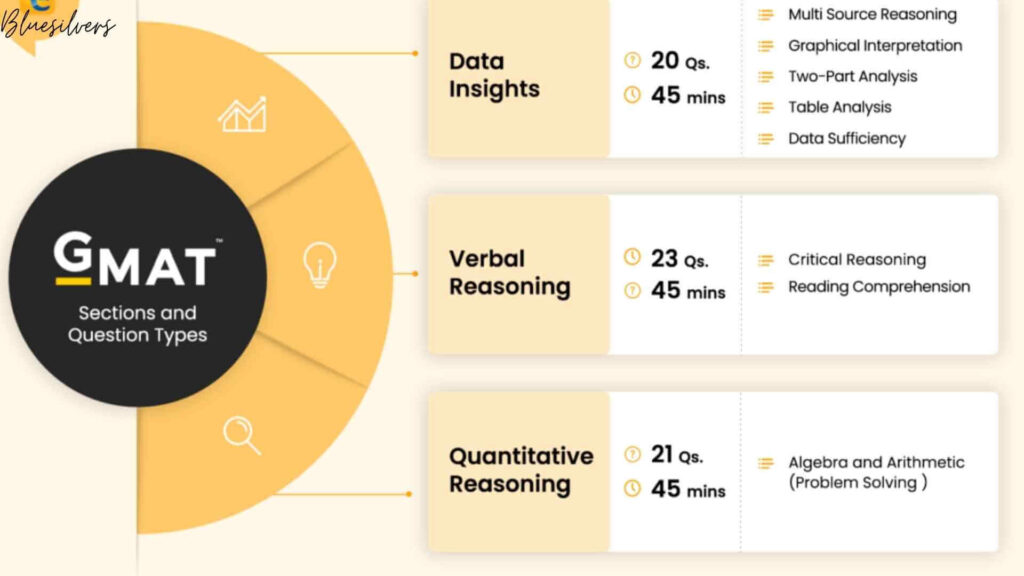
The GMAT Integrated Reasoning section consists of 12 questions to be completed in 30 minutes. These questions are divided into four distinct types: Table Analysis, Graphics Interpretation, Multi-Source Reasoning, and Two-Part Analysis. Each question type assesses specific analytical skills, and understanding the nuances of each is crucial for effective preparation.
1. Table Analysis

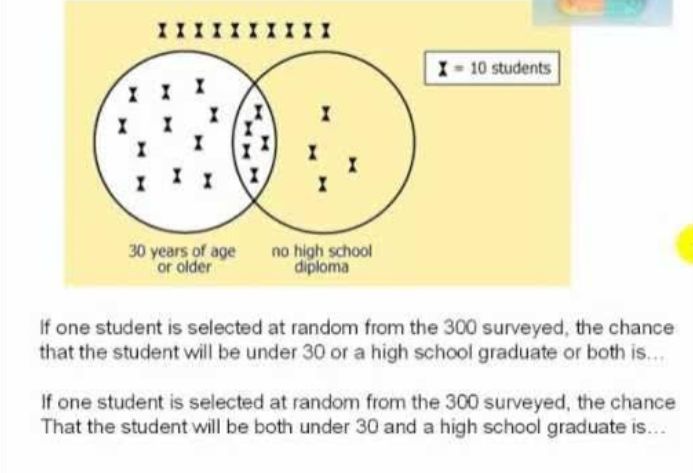
Table Analysis questions present data in a sortable table format, similar to a spreadsheet. Candidates are required to analyze the data to determine whether certain statements are accurate. This involves discerning relevant information, recognizing patterns, and making logical inferences.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Ability to interpret and manipulate tabular data.
- Critical evaluation of statements based on data analysis.
Strategies for Success:
- Familiarize yourself with sorting and filtering data to quickly locate pertinent information.
- Practice identifying trends and outliers within datasets.
2. Graphics Interpretation
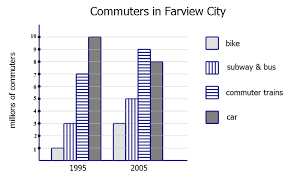
Graphics Interpretation questions require candidates to interpret data presented in graphical formats, such as bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, or pie charts. You will complete statements by selecting the appropriate options from drop-down menus based on the graphical data.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Understanding and interpreting various graphical data representations.
- Drawing accurate conclusions from visual data.
Strategies for Success:
- Develop proficiency in reading different types of graphs and charts.
- Pay attention to units of measurement and scales to ensure accurate interpretation.
3. Multi-Source Reasoning
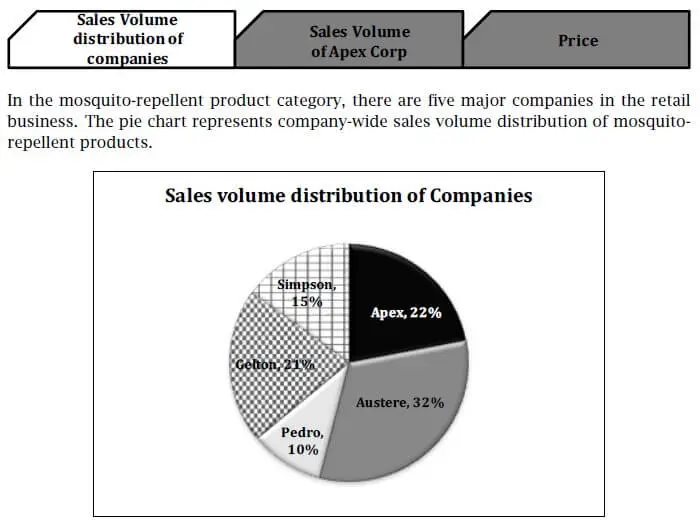
Multi-Source Reasoning questions involve analyzing information from multiple sources, such as text passages, tables, or graphs, presented on multiple tabs. Candidates must integrate and synthesize this information to answer questions, which may be in multiple-choice or true/false formats.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Ability to integrate information from diverse formats and sources.
- Critical thinking and logical reasoning.
Strategies for Success:
- Practice toggling between different information sources efficiently.
- Enhance skills in synthesizing information to form well-reasoned conclusions.
4. Two-Part Analysis
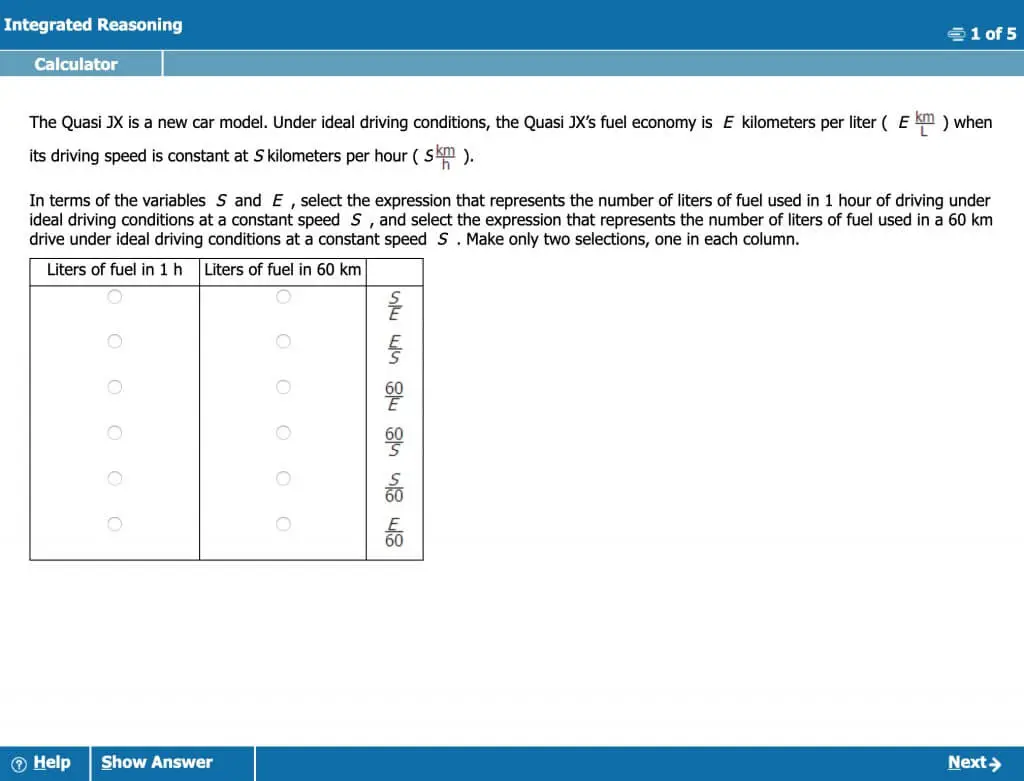
Two-Part Analysis questions assess your ability to solve complex problems that require simultaneous consideration of two components. These questions may involve quantitative, verbal, or a combination of both skills. You will select answers from a table with a column for each part, ensuring that both selections satisfy the given conditions.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Simultaneous evaluation of dual components in a problem.
- Flexibility in handling diverse problem types and formats.
Strategies for Success:
- Practice breaking down complex problems into manageable parts.
- Ensure that both selected answers are consistent with each other and the problem’s requirements.
General Tips for Excelling in the Integrated Reasoning Section

- Time Management: With only 30 minutes for 12 questions, efficient time management is crucial. Allocate time based on question complexity and avoid spending too long on any single question.
- Practice with Diverse Data Formats: Exposure to various data presentations, such as charts, graphs, and tables, will enhance your ability to interpret and analyze information swiftly.
- Develop Analytical Skills: Strengthen your critical thinking and analytical abilities through practice problems and real-world data analysis.
- Utilize Official Resources: Make use of official GMAT preparation materials to familiarize yourself with the question formats and difficulty level.
In conclusion, the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section of the GMAT is designed to assess skills that are vital in the modern business landscape. By understanding the distinct question types and honing the relevant analytical abilities, candidates can enhance their performance and demonstrate their capacity to handle complex, data-driven decision-making processes.
To get more about GMAT Integrated Reasoning questions, please click