All About GMAT Verbal Reasoning
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a standardized assessment widely used by business schools to evaluate the qualifications of applicants for advanced study in business and management. A critical component of the GMAT is the Verbal Reasoning section, which measures a candidate’s ability to read and comprehend written material, reason and evaluate arguments, and correct written material to conform to standard written English.
Table of Contents
Structure of the GMAT Verbal Reasoning Section
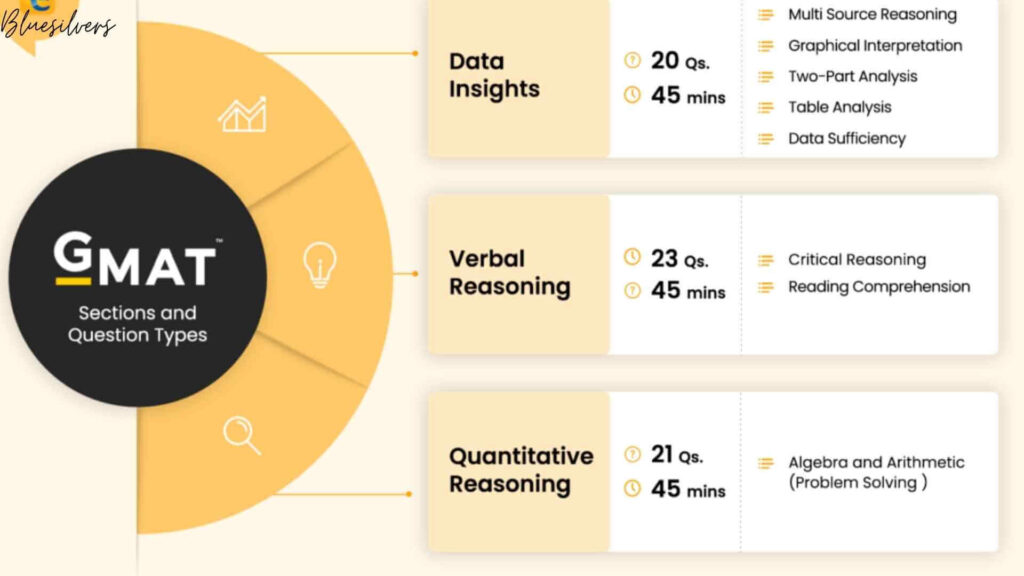
The Verbal Reasoning section consists of 23 multiple-choice questions to be completed in 45 minutes. These questions are designed to assess critical reading skills, argument analysis, and grammatical proficiency. The section includes two primary question types: Reading Comprehension and Critical Reasoning.
Question Types

- Reading Comprehension: Reading Comprehension questions evaluate your ability to understand, interpret, and apply information from written passages. These passages cover a range of topics, including social sciences, natural sciences, business, and humanities. After reading a passage, you’ll answer questions that test your understanding of the main idea, supporting details, logical structure, and the author’s tone and purpose.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Understanding of the main idea and supporting details.
- Ability to make inferences based on the text.
- Recognition of logical relationships within the passage.
Strategies for Success:
- Practice active reading by summarizing paragraphs and noting the author’s intent.
- Focus on understanding the structure and organization of the passage.
- Avoid bringing outside knowledge into your interpretations; base answers solely on the passage content.
- Critical Reasoning: Critical Reasoning questions assess your ability to analyze arguments, identify assumptions, evaluate evidence, and determine the strength of conclusions. These questions typically present a short argument followed by a question prompt, such as identifying the argument’s assumption, strengthening or weakening the argument, or identifying a flaw in the reasoning.
Key Skills Assessed:
- Ability to identify premises and conclusions.
- Evaluation of the argument’s logical structure.
- Identification of underlying assumptions and potential weaknesses.
Strategies for Success:
- Clearly distinguish between the argument’s premises and conclusion.
- Consider alternative explanations or counterexamples that could weaken the argument.
- Practice identifying common logical fallacies and argument patterns.
Preparation Tips

- Develop a Reading Habit: Regularly read complex materials, such as academic journals, business articles, and literature, to enhance comprehension skills and familiarize yourself with diverse writing styles.
- Practice Critical Thinking: Engage in activities that require analysis and evaluation of arguments, such as debates or writing analytical essays, to strengthen critical reasoning abilities.
- Review Grammar Rules: Ensure a solid understanding of standard English grammar, including sentence structure, verb usage, and punctuation, to excel in sentence correction questions.
- Take Practice Tests: Simulate test conditions with timed practice tests to build stamina and improve time management skills.
- Analyze Mistakes: Review incorrect answers to understand your mistakes and learn from them, focusing on areas that need improvement.
Time Management

Efficient time management is crucial in the Verbal Reasoning section. Allocate approximately two minutes per question, but remain flexible, as some questions may require more or less time. If a question is particularly challenging, make an educated guess and move on to ensure all questions are addressed within the allotted time.
Conclusion
The GMAT Verbal Reasoning section is designed to assess skills essential for success in business school and management careers. By understanding the structure and types of questions, and by implementing effective preparation strategies, you can enhance your performance in this section. Consistent practice, critical analysis, and a thorough understanding of English grammar and usage will contribute significantly to achieving a high score on the Verbal Reasoning section.