Introduction
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a standardized exam designed to assess the skills required for success in graduate business programs, such as Master of Business Administration (MBA) and other management-related degrees. Administered by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), the GMAT is widely recognized by business schools worldwide. This guide provides a detailed overview of the GMAT, including its structure, scoring, preparation strategies, and tips for success.
Purpose of the GMAT
The GMAT evaluates a candidate’s ability to think critically, solve problems, and analyze data—skills essential for graduate-level business studies. Business schools use GMAT scores to assess applicants’ readiness for challenging academic programs and their potential for success in management roles.
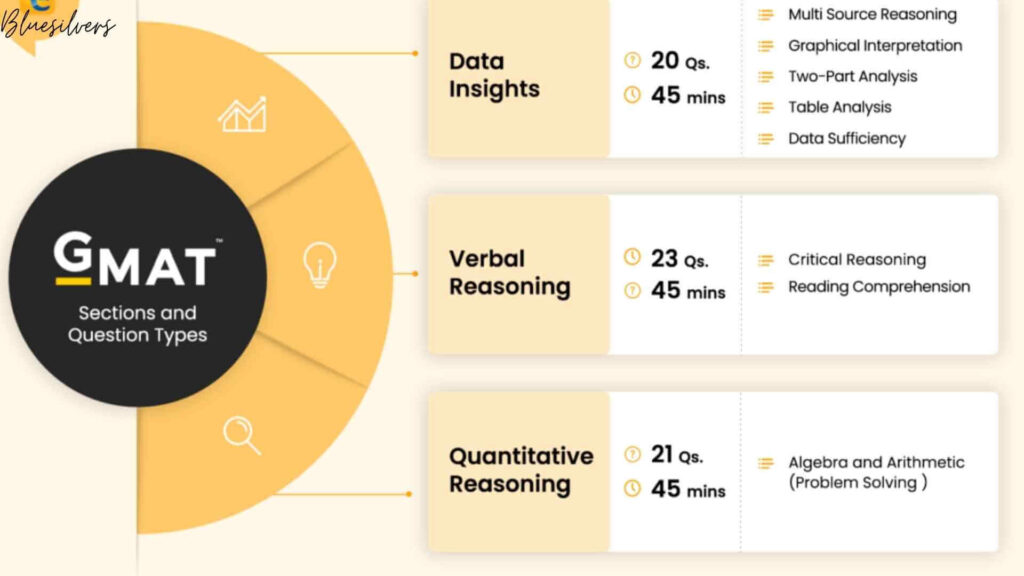
GMAT Exam Structure
The GMAT consists of four main sections:
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
- Duration: 30 minutes
- Question Type: One essay task (Analysis of an Argument)
- Purpose: Evaluates your ability to critically analyze an argument and communicate ideas clearly.
- Integrated Reasoning (IR)
- Duration: 30 minutes
- Number of Questions: 12
- Question Types: Multi-source reasoning, graphics interpretation, table analysis, and two-part analysis.
- Purpose: Tests the ability to evaluate information presented in different formats, such as graphs, tables, and charts.
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Duration: 62 minutes
- Number of Questions: 31
- Question Types:
- Problem Solving: Tests mathematical skills and logical reasoning.
- Data Sufficiency: Requires analyzing data to determine if sufficient information is provided to solve a problem.
- Purpose: Measures numerical and mathematical abilities, including algebra, geometry, and arithmetic.
- Verbal Reasoning
- Duration: 65 minutes
- Number of Questions: 36
- Question Types:
- Reading Comprehension: Tests the ability to understand and analyze written material.
- Critical Reasoning: Evaluates logical reasoning and argument evaluation skills.
- Sentence Correction: Focuses on grammar, sentence structure, and clarity.
- Purpose: Assesses the ability to read critically, evaluate arguments, and correct language errors.
GMAT Scoring System
- Total Score: Ranges from 200 to 800 (based on Quantitative and Verbal sections).
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA): Scored on a scale of 0 to 6.
- Integrated Reasoning (IR): Scored on a scale of 1 to 8.
- Quantitative and Verbal Sections: Scaled scores range from 0 to 60 each.
- Percentile Ranking: Reflects how your score compares to other test-takers.
How to Prepare for the GMAT
- Understand the Test Format: Familiarize yourself with the test structure, question types, and timing constraints.
- Develop a Study Plan: Allocate sufficient time (2–3 months) for preparation. Focus on weaker areas and gradually increase practice intensity.
- Use Official GMAT Materials: GMAC provides official practice exams and sample questions to simulate real test conditions.
- Practice Regularly: Take mock tests to improve speed, accuracy, and endurance. Analyze mistakes to refine strategies.
- Focus on Time Management: Practice solving questions within time limits to avoid running out of time during the test.
- Seek Professional Help: Consider enrolling in GMAT prep courses or hiring a tutor for personalized guidance.
Tips for Success
- Read Questions Carefully: Avoid assumptions and misinterpretations by analyzing each question thoroughly.
- Skip Difficult Questions Temporarily: Don’t spend too much time on one question. Move forward and return to it later if needed.
- Memorize Formulas and Concepts: Focus on mathematical formulas and grammar rules to save time during the test.
- Use the Process of Elimination: Eliminate incorrect answer choices to increase the chances of selecting the right one.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: Manage stress effectively by practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques before the exam.
GMAT Registration and Fees
- Registration Fee: $275 USD (varies slightly by location).
- Rescheduling Fee: Additional charges apply for rescheduling or canceling the exam.
- Test Availability: Offered year-round at test centers or online.
- Retakes: Candidates can retake the exam after 16 days, up to five times per year and eight times in total.
Who Should Take the GMAT?
- MBA Aspirants: Most business schools require GMAT scores for admission.
- Business Professionals: Those seeking career advancement through executive MBA programs.
- International Students: Candidates planning to study abroad in top business schools.
Conclusion
The GMAT is a globally recognized exam that measures critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and problem-solving skills. Its structured format and scoring system provide business schools with a reliable assessment of candidates’ potential for academic success. Effective preparation through mock tests, practice materials, and time management strategies can significantly improve performance. Whether pursuing an MBA, a master’s degree, or advancing in your career, achieving a high GMAT score can open doors to prestigious programs and promising opportunities.




Pingback: How much is GMAT exam in Nigeria - Extremely affordable
Register for the GMAT exam with Bluesilvers consulting