All You Need to Know About GRE
The Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is a standardized test widely used for admissions into graduate and business schools across the globe. Administered by the Educational Testing Service (ETS), the GRE assesses verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, analytical writing, and critical thinking skills. It is designed to evaluate readiness for advanced academic work and is accepted by thousands of programs worldwide.
To excel in the GRE, familiarize yourself with each of the GRE question types, as this knowledge is crucial for effective test preparation.
Table of Contents
Structure of the GRE
The GRE General Test consists of three main sections:
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA):
- Comprises two tasks: “Analyze an Issue” and “Analyze an Argument.”
- Measures the ability to articulate thoughts, provide logical arguments, and support ideas with examples.
- Each task is timed for 30 minutes.
- Verbal Reasoning:
- Focuses on reading comprehension, sentence equivalence, and text completion.
- Tests vocabulary usage, understanding of complex texts, and reasoning abilities.
- Contains two sections, each lasting 30 minutes with approximately 20 questions per section.
- Quantitative Reasoning:
- Measures mathematical skills, problem-solving abilities, and data interpretation.
- Topics include arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and data analysis.
- Consists of two sections, each lasting 35 minutes with about 20 questions per section.
In addition to the above, the GRE may include experimental or research sections that are not scored but used for ETS research purposes.
Each of the GRE question types has unique characteristics, making it essential to develop tailored preparation strategies for success.
GRE Question Types
Understanding the different GRE question types can significantly aid in your preparation for the exam. By familiarizing yourself with the GRE question types, you can develop strategies tailored to each section.
The analytical writing section includes two main GRE question types: analyzing an issue and analyzing an argument, both critical for demonstrating your reasoning skills.
1. Analytical Writing Questions
In verbal reasoning, knowing the GRE question types helps improve your performance in understanding, interpreting, and analyzing written texts.
- Analyze an Issue: Requires test-takers to evaluate a statement or claim and present a logical argument discussing its strengths and weaknesses.
- Analyze an Argument: Involves critiquing an argument, identifying logical flaws, and providing evidence to either support or dispute the claim.
- Focuses on writing clarity, structure, logical reasoning, and supporting evidence.
Understanding what to expect from the GRE question types will help streamline your study efforts and make for a more efficient preparation process.
Familiarity with the GRE question types in quantitative reasoning can lead to better problem-solving skills, allowing you to tackle different question formats effectively.
Mastering the GRE question types allows you to approach practice questions with a more strategic mindset, enhancing your chances of success.
2. Verbal Reasoning Questions
- Reading Comprehension:
- Tests the ability to understand, interpret, and analyze written passages.
- Questions ask about main ideas, specific details, assumptions, and inferences.
- Passages can range from one paragraph to several, covering topics in humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- Text Completion:
- Requires filling in blanks within sentences or paragraphs.
- Options are provided for each blank, and correct answers depend on contextual understanding.
- Focuses on vocabulary, grammar, and logical flow.
- Sentence Equivalence:
- Involves selecting two words or phrases that create grammatically and contextually equivalent sentences.
- Tests vocabulary knowledge and sentence structure.
3. Quantitative Reasoning Questions
- Quantitative Comparison:
- Compares two quantities and asks whether one is greater, less, equal, or if the relationship cannot be determined.
- Tests analytical and logical reasoning rather than complex calculations.
- Problem-Solving Questions:
- Standard multiple-choice questions, where test-takers must choose one correct answer.
- Some questions allow for multiple answers, and all correct options must be selected.
- Data Interpretation:
- Involves analyzing charts, graphs, and tables to answer questions.
- Tests data analysis and pattern recognition skills.
- Numeric Entry Questions:
- Requires test-takers to input numeric answers rather than selecting from given choices.
Scoring System
- Verbal and Quantitative Sections: Scores range from 130 to 170 in 1-point increments.
- Analytical Writing: Scored on a scale of 0–6 in half-point increments.
- Total GRE scores combine the Verbal and Quantitative sections, resulting in a composite score ranging from 260 to 340.
- Scores remain valid for five years after the test date.
GRE Subject Tests
In addition to the General Test, ETS offers GRE Subject Tests in specific fields, including Biology, Chemistry, Literature in English, Mathematics, Physics, and Psychology. These tests are intended for students with specialized knowledge and are used by certain programs for admissions.
Registration and Fees
By recognizing the GRE question types, you can allocate your study time effectively, focusing on areas that need improvement.
- Registration for the GRE can be done online via the ETS website.
- The test is offered year-round at Prometric test centers worldwide.
- Fees vary by location but typically range around $205–$230.
- Additional costs may apply for rescheduling or sending score reports to extra schools.
Test Preparation
Preparation for the GRE requires focused study and practice. Many test-takers invest in:
Identifying the GRE question types that will appear on your test is a vital step in your preparation strategy.
Each GRE question type serves a specific purpose and evaluates distinct skill sets, so thorough knowledge will benefit test-takers significantly.
When preparing, prioritize understanding the GRE question types to improve your overall performance on the test day.
- Official GRE Study Guides and ETS Practice Tests.
- Online courses and coaching programs.
- GRE prep apps for mobile devices.
- Flashcards to improve vocabulary.
Practicing under timed conditions is essential for improving pacing and performance.
Who Should Take the GRE?
The GRE is suitable for:
- Students seeking admission to graduate programs (e.g., master’s or doctoral degrees).
- Candidates applying to MBA programs or business schools that accept GRE scores instead of GMAT.
- Individuals looking to demonstrate academic readiness for specialized certifications or fields of study.
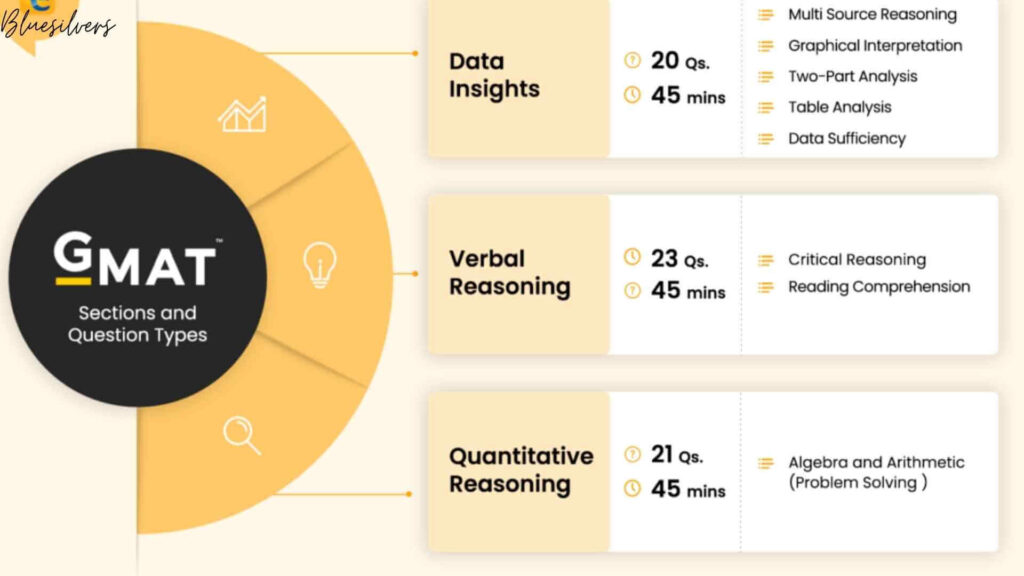
GRE vs GMAT
Many students debate whether to take the GRE or GMAT, especially for business school admissions. Key differences include:
A thorough understanding of GRE question types ensures you approach each section with confidence and competence, ultimately leading to higher scores.
- GRE is broader and used for various graduate programs, whereas GMAT is primarily for MBA admissions.
- GRE emphasizes verbal and analytical writing, while GMAT focuses on quantitative and integrated reasoning.
Strategies for Success
- Develop a Study Plan: Begin preparation at least 3–6 months in advance.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Use diagnostic tests to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Practice Regularly: Solve practice questions to improve speed and accuracy.
- Time Management: Learn to allocate time effectively during the test.
- Take Mock Tests: Simulate test-day conditions to build confidence.
Test Day Tips
- Arrive at the test center at least 30 minutes early.
- Carry a valid photo ID and admission ticket.
- Bring acceptable calculators as per ETS guidelines.
- Stay calm, focused, and pace yourself throughout the exam.
Conclusion
The GRE is a versatile and widely accepted test for graduate admissions, assessing essential skills required for academic success. Proper planning, preparation, and practice can significantly improve scores and help secure admission to desired programs. Whether pursuing a master’s, doctoral degree, or business school, the GRE provides an opportunity to showcase readiness for advanced education.