GMAT Syllabus: A Comprehensive Guide
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a globally recognized exam designed to assess skills essential for success in graduate business programs, including MBA and Master’s in Finance. It evaluates analytical, reasoning, verbal, and quantitative skills required for management studies. Understanding the GMAT syllabus is crucial for effective preparation and success in the exam.
Overview of the GMAT Exam
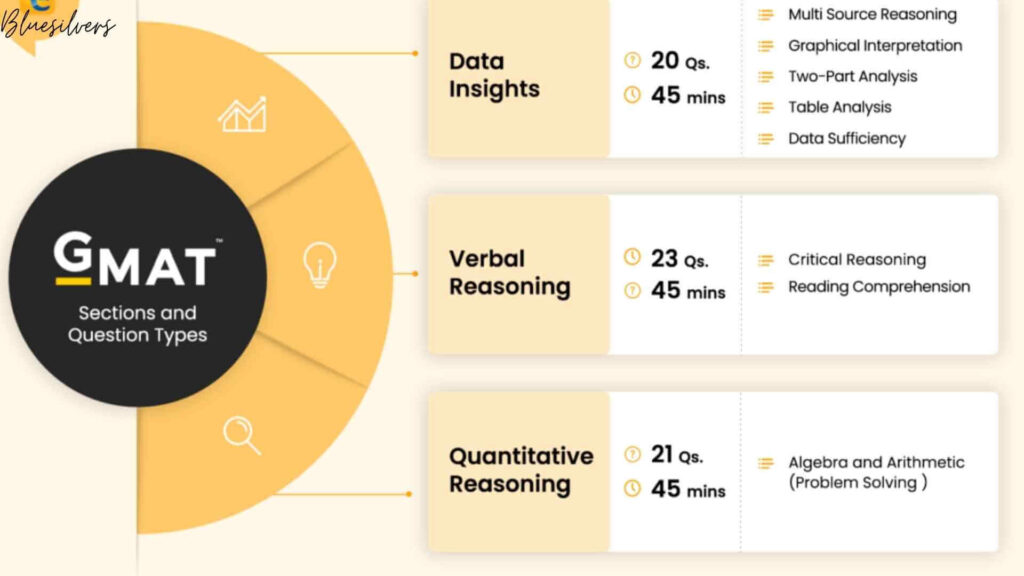
The GMAT exam is divided into four sections, each designed to measure specific skills:
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
- Integrated Reasoning (IR)
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
Each section contributes to a candidate’s overall performance and score. Let’s explore each section of the GMAT syllabus in detail.
1. Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
Duration: 30 minutes
Number of Questions: 1 essay
Score Range: 0–6
Purpose:
The AWA section tests the ability to critically evaluate arguments and express ideas clearly. Candidates must analyze an argument, identify flaws, and provide a logical critique.
Syllabus Focus:
- Analyzing an Argument
- Evaluating evidence and reasoning
- Identifying logical flaws in arguments
- Structuring and organizing ideas effectively
Sample Task:
Analyze the reasoning behind an argument and critique its strengths and weaknesses.
Preparation Tip:
Practice essay writing, focusing on grammar, coherence, and logical organization of ideas.
2. Integrated Reasoning (IR)
Duration: 30 minutes
Number of Questions: 12
Score Range: 1–8
Purpose:
This section assesses the ability to interpret and analyze data presented in different formats, such as tables, charts, and graphs. It evaluates decision-making skills required in business scenarios.
Syllabus Focus:
- Table Analysis: Analyzing data in tables and identifying relevant information.
- Graphics Interpretation: Understanding charts and graphs.
- Multi-Source Reasoning: Evaluating data from multiple sources to answer questions.
- Two-Part Analysis: Solving complex problems involving two steps.
Sample Question:
Analyze a graph showing sales trends and answer questions about performance patterns.
Preparation Tip:
Familiarize yourself with graphs, tables, and data interpretation techniques.
3. Quantitative Reasoning
Duration: 62 minutes
Number of Questions: 31
Score Range: 6–51
Purpose:
This section measures mathematical skills and the ability to interpret and analyze quantitative data. It focuses on problem-solving and data sufficiency.
Syllabus Focus:
- Arithmetic: Integers, fractions, percentages, ratios, and averages.
- Algebra: Linear equations, quadratic equations, and inequalities.
- Geometry: Lines, angles, circles, triangles, and coordinate geometry.
- Word Problems: Application of mathematical concepts to real-life problems.
Types of Questions:
- Problem Solving: Solving mathematical problems using logic and formulas.
- Data Sufficiency: Determining whether the given data is sufficient to answer a question.
Sample Question:
If x + y = 12 and x – y = 4, find the value of x and y.
Preparation Tip:
Memorize formulas and practice solving problems quickly under time constraints.
4. Verbal Reasoning
Duration: 65 minutes
Number of Questions: 36
Score Range: 6–51
Purpose:
This section evaluates reading comprehension, critical reasoning, and sentence correction skills. It tests the ability to understand and analyze written content.
Syllabus Focus:
- Reading Comprehension:
- Understanding passages and answering related questions.
- Identifying main ideas, supporting details, and implications.
- Critical Reasoning:
- Evaluating arguments and identifying assumptions or weaknesses.
- Strengthening or weakening an argument.
- Sentence Correction:
- Correcting grammatical errors and improving sentence structure.
- Ensuring clarity, conciseness, and proper word usage.
Sample Question:
Which of the following sentences is grammatically correct?
A) The team has completed their project.
B) The team has completed its project. (Correct Answer)
Preparation Tip:
Practice grammar rules and read articles to improve comprehension skills.
Scoring System
- Total Score: 200–800 (Quantitative and Verbal sections contribute).
- AWA Score: 0–6 (Evaluated separately).
- IR Score: 1–8 (Evaluated separately).
Test Duration and Format
- Total Time: About 3 hours and 7 minutes (including breaks).
- Adaptive Format: The test adjusts the difficulty of questions based on performance.
Key Preparation Strategies
- Understand the Format: Familiarize yourself with the syllabus and question types.
- Develop Time Management Skills: Allocate specific time for each section during practice.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify challenging topics and dedicate extra practice time.
- Take Practice Tests: Simulate exam conditions to build stamina and track performance.
- Review Mistakes: Analyze errors and learn strategies to avoid them in the future.
Conclusion
The GMAT syllabus covers essential skills in analytical writing, data interpretation, quantitative problem-solving, and verbal reasoning. Each section tests a different aspect of a candidate’s abilities, ensuring they are prepared for the demands of business school programs. A thorough understanding of the syllabus and consistent preparation using official study materials and practice tests can help candidates achieve a competitive score. Whether you’re aiming for an MBA or a specialized master’s degree, excelling in the GMAT opens doors to top business schools worldwide.